Here at Levi9, we’re always looking to see what’s next in tech. Currently, of course, that means diving deep into the massive waves AI is making, especially when it comes to tools for handling data.
What’s striking is how AI simplifies the user journey and democratizes data access. Now, even a decision-maker with zero coding experience can gain rapid insights, simply because the barrier to entry has dropped to a natural language chat interface.
This significant shift has led to two very common requests from our clients:
- They need faster access to analytics. To tackle this, we’ve been busy building text-to-SQL or text-to-API solutions, pairing Large Language Models (LLMs) with MCP servers.
- They want to automate the ETL workflow. Data landscapes are complex. Clients want to describe the required Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) process in plain human language, then let the AI handle all the heavy lifting of actually building the workflow.
With this in mind, I was curious what existing tools are available on the market. And I focused my attention on one of them, the Knime Analytics Platform.
What is Knime Analytics Platform?
What first drew my attention to Knime is that it’s an open-source platform with an enormous amount of extensions and customizations. The functionality spans the entire data and machine learning lifecycle: from data access and ETL to creation of ML models and autonomous agents.
The core idea is visual programming – essentially a drag-and-drop interface, shown below.
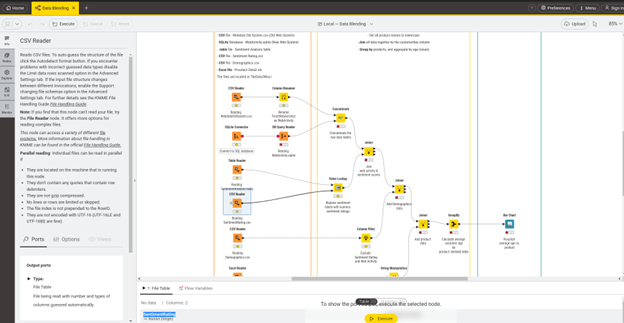
In the center, the Workflow Editor is located, which is responsible for building and interacting with data pipelines. On the left, we can see Node Explorer, where all building blocks are located, and other menu options, such as K-AI – the AI chat with the entire KNIME, which we will discuss later. At the bottom of the screen, Console and Node Monitor – tools for analysing and debugging your workflow.
It reminded me a bit of Jupyter Notebook, which combines text description and code with visualisations. In the case of KNIME, we have visualisation nodes instead of the code.
With limited knowledge of programming languages, users can use these building blocks to create a comprehensive, production-ready workflow. Of course, for those times when you need deep customization or are tackling a really complex workflow, you can always reach for Python or R, which are commonly used for data workloads and supported in KNIME.
First steps
After downloading the KNIME, here are the essential first steps:
- Linux-specific fix: If using KNIME for Linux, use the “DK_BACKEND=x11 ./knime ” command to run the app, as it avoids some issues related to chat interactions.
- Extract additional extensions:Go to Menu -> Install Extensions. And choose the needed ones. I recommend KNIME AI, Database, and Labs Extensions, as they cover most LLM interactions and add additional nodes to the workflows. Personally, I installed all the available extensions, as I was curious about the possibilities provided by Knime Community.
- Access example workflows: In the education part of courses, KNIME provides ready-to-test workflows that you can download and use. For example, the RAG workflow is there.
How KNIME Works: Core Concepts
The main building blocks that form our ETL process in KNIME are:
- Nodes: the atomic units of a KNIME workflow. Each node encapsulates a specific function, such as reading a file, filtering rows, training a model, or creating a visualisation.
- Ports and Connections: Nodes possess input and output ports, which dictate how they interact with each other. Data, models, and other objects flow from an output port of one node to the input port of another through connections drawn in the Workflow Editor.
- Workflows: A workflow is the complete, executable representation of a data process, formed by a sequence of connected nodes. Because every transformation step is an explicit, visible node, the workflow itself becomes a form of documentation.
- Components and Metanodes: These mechanisms manage complexity and promote reusability. Metanodes are simple containers that group a selection of nodes into a single node, helping to reduce visual clutter in large workflows. Components, however, are far more powerful. They are reusable, shareable nodes that can be created from a workflow segment. Components can have their own custom configuration dialogues and interactive composite views, effectively allowing users to build their own nodes. It`s a reusable asset that can be shared via the KNIME Hub.
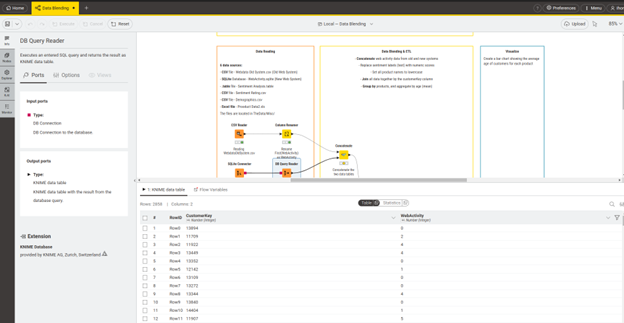
The ability to use the Node Monitor to view the full data table at the output of any node provides a tool for debugging, validation, and understanding. A user can immediately see the effect of the operations and transformations inside it:
Advanced Analytics: Automation and Flow Control
Real-world data processes are rarely simple, linear sequences. They often require repetition, conditional logic, and the ability to handle unexpected errors. KNIME offers a sophisticated set of flow control nodes that enable users to construct dynamic, automated workflows that can model complex business logic without requiring code.
These nodes include:
- Flow Variables are the key to dynamic workflows. These are parameters within the workflow that can be used to dynamically override the configuration settings of downstream nodes. For example, a flow variable could hold a file path, a date, or a filter condition.
- Automating with loops is the cornerstone of automation, allowing a segment of a workflow to be executed repeatedly.
- Conditional Execution with Switches directs the flow of a workflow based on specific conditions. The IF Switch node creates two output branches (top and bottom) and, based on a condition, passes data only through the active branch. The active port can be selected manually or, more powerfully, controlled by a flow variable. Similarly, the CASE Switch node provides three or more branches, allowing for more complex conditional logic.
- Robust Error Handling: Try and Catch Errors nodes provide a robust error-handling mechanism. Any nodes placed between a Try node and a Catch Errors node are monitored. If any node in this “try” block fails during execution, the workflow continues. Instead, control is passed to a separate “catch” branch, which can perform alternative actions, such as logging the error or sending a notification email.
Real business processes involve repetition, like generating a report every month, conditional logic, applying different tax calculations for different regions, and the potential for failure such as a database being temporarily offline. KNIME’s flow control nodes provide direct visual analogues for these business concepts.
How KNIME Integrates Generative AI
KNIME integrates GenAI in several ways, from workflow assistance to autonomous agents. Let’s look at them closely.
K-AI assistant
KNIME has integrated an AI assistant called K-AI. It helps in two huge ways:
- Q&A Mode: You can ask, “How do I filter by date?” and it will point you to the right node.
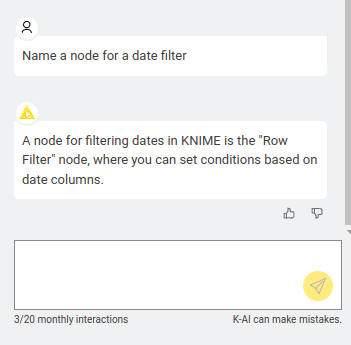
- Build Mode: You can say, “Generate a bar chart to display a growth rate over the months”, and it will actually drag the nodes onto the canvas and connect them for you. It can create an entirely new workflow and extend existing ones.
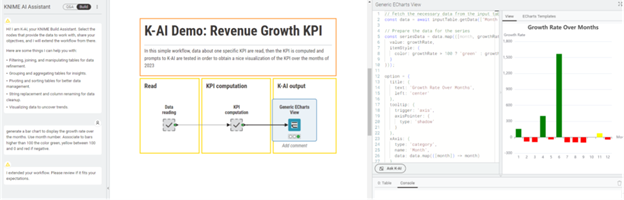
This integration makes building and managing complex data workflows significantly faster and more intuitive for users of all skill levels.
What is important – you have only 20 K_AI interactions per month. If you need more, you need to go with a paid plan.
RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) Systems
By using the community extensions, you can also build complete RAG systems, from creating the vector database to optimising the retrieval for the best results. Below are examples of workflows that we downloaded earlier in this article:
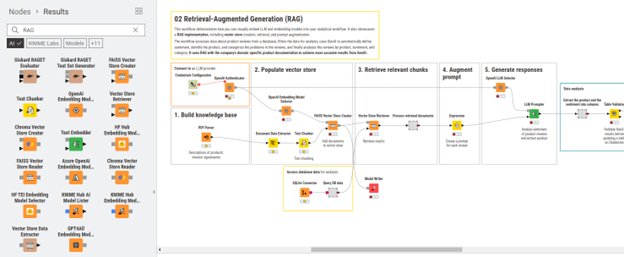
These examples provide a practical starting point for implementing RAG with KNIME. You can adapt and expand upon these workflows to integrate powerful AI capabilities into your data analysis projects.
Autonomous Agents
Agentic Artificial Intelligence (Agentic AI) systems are designed for autonomous operation, focused on achieving specific objectives. These agents are capable of executing tasks, making independent decisions, and modifying their strategy in response to new data.
KNIME integrates Agent possibilities into its workflows, allowing users to build and deploy an agentic system directly in the workflow.
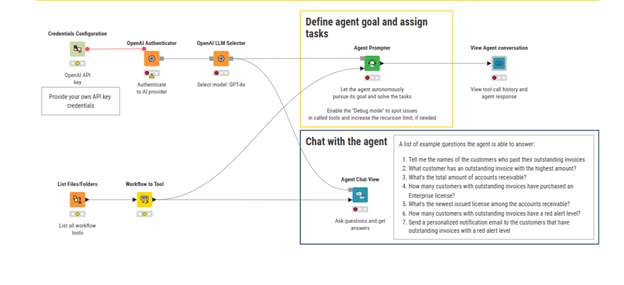
What was also essential for me to know is that KNIME allows for the integration of Model Context Protocol in such agent workflows. However, setting up an MCP in KNIME is more complex than in programming languages like Python, which offer specific libraries. In KNIME, you must:
- Configure your workflow to accept clearly defined inputs.
- Ensure it produces structured, machine-readable outputs (such as JSON).
- Expose the workflow via REST through the KNIME Business Hub.
- Create a simple tool description file that follows the MCP tool schema, detailing the tool’s function and usage.
Of course, it’s a downside, but it’s acceptable for such a big system that integrates many processes into one application.
KNIME Pricing
The Free KNIME option is perfect if you’re exploring analytics, experimenting with workflows, or building prototypes locally. However, the moment you need automation, cloud execution, team collaboration, deployment as REST endpoints or data apps, or version-controlled workflows, the Free tier becomes limiting, and you must upgrade to a paid tier. Below is a short price comparison:
Feature | Free (Desktop) | Pro (Cloud) |
Price | $0/month — fully free & open-source | From $19/month (€19) |
Workflow building | Build & run workflows locally; connect to 300+ data sources | Full workflow building + cloud execution + deployment |
Execution & automation | Manual execution only; runs on your machine | Automated cloud execution (120 credits included; then $0.025/min) |
Deployment | No native deployment; sharing is limited to files | Deploy workflows as data apps or REST services; email alerts |
Versioning & storage | Local workflows only; no cloud history | Unlimited versioning; secure cloud secrets; 30GB storage |
K-AI assistant | 20 interactions/month | 500 interactions/month + PAYG expansion |
There are also team and business plans available, and they are more focused on team collaboration and governance.
Final thoughts
After exploring KNIME, my overall impression is positive, particularly in light of the current demand for accelerated data workflows and AI integration.
The platform is powerful in the data processing and machine learning space. Its core strength lies in its visual programming paradigm. It successfully democratizes data science, making complex ETL, analysis, and even basic machine learning accessible to users who aren’t fluent in Python or R. The drag-and-drop workflow editor is intuitive, and the concept of nodes, ports, and workflows makes the entire process more or less self-documenting and easy to debug—a significant advantage over script-based methods.
Areas for Improvement that I noticed:
- Learning Curve for Optimisation: While KNIME is a no-code/low-code platform, users still require training to build optimal and easily understandable workflows.
- Workflow Complexity and maintainability: Despite visualisation tools, complex workflows can still be complicated to edit or extend. Although K–AI assists, screens can become overly crowded with elements.
- Complex MCP Integration: Integrating with MCP servers (as previously mentioned) presents a degree of complexity.
In conclusion, the KNIME Analytics Platform is more than just an ETL tool; it’s a comprehensive visual platform that lowers the entry barrier into data science.
For organizations seeking to accelerate their pace and provide decision-makers with direct access to data insights without relying on a large team of data engineers, KNIME is a solution well worth exploring.
Let's Talk About Your Data Journey
At Levi9, we help organizations turn complex data challenges into competitive advantages. Whether you’re exploring platforms like KNIME, building AI-powered workflows, or looking to democratize data access across your teams, our data engineering experts can guide you from evaluation to implementation. Let’s discuss how we can accelerate your analytics journey, reach out to our team today.